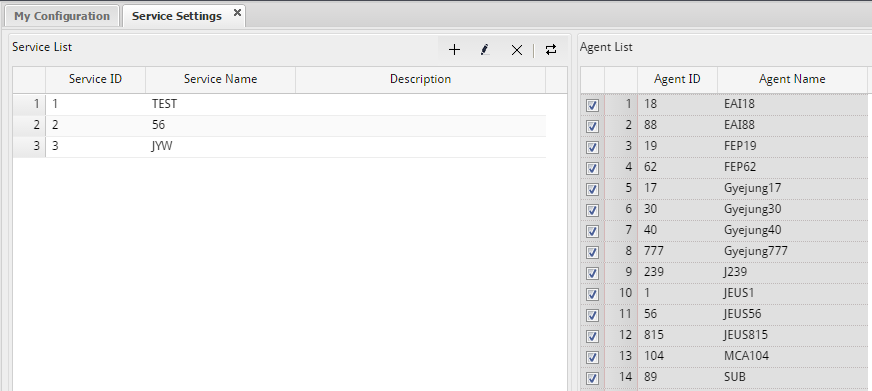
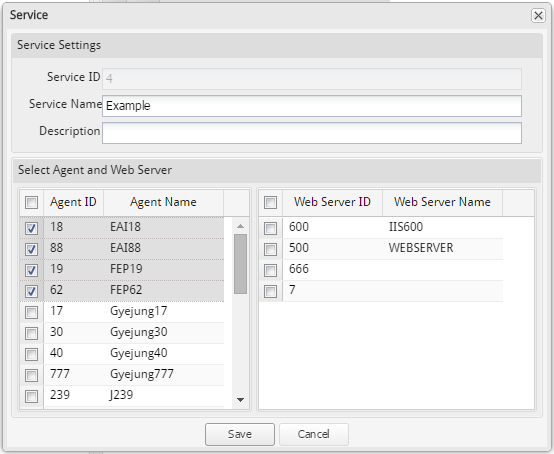
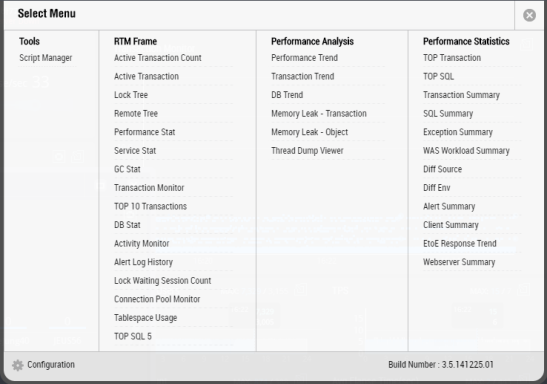
Overview
MaxGauge is a performance management tool designed to provide an integrated and effective management of performance and system errors of WAS and the Database server, which make up the N-tier web service environment. From a system operation manager’s perspective, the ability to connect and integrate WAS and DB for monitoring is essential for an effective web service performance management.
MaxGauge supports system administrators or database and application managers who are responsible for system errors and performance management, to effectively carry out their tasks of real-time monitoring, diagnosis, and analysis.
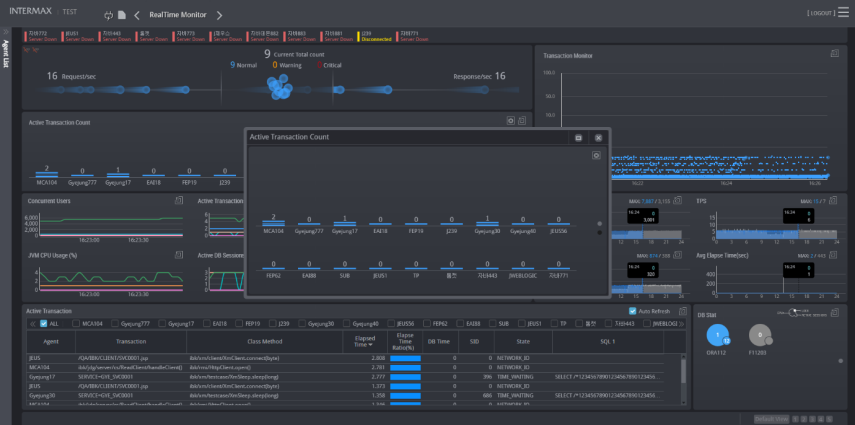
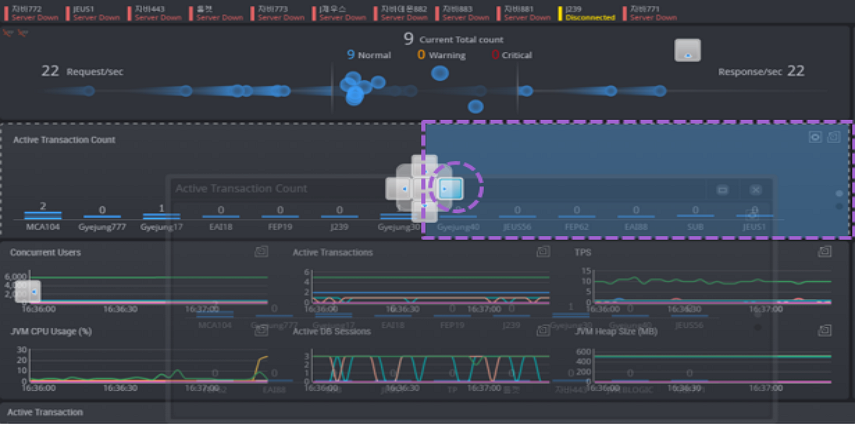
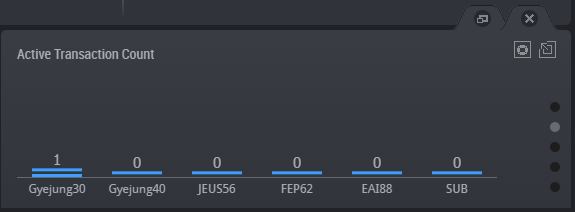
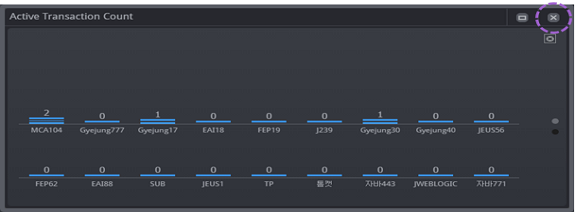
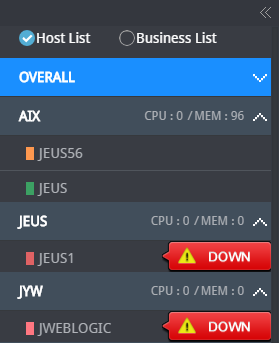
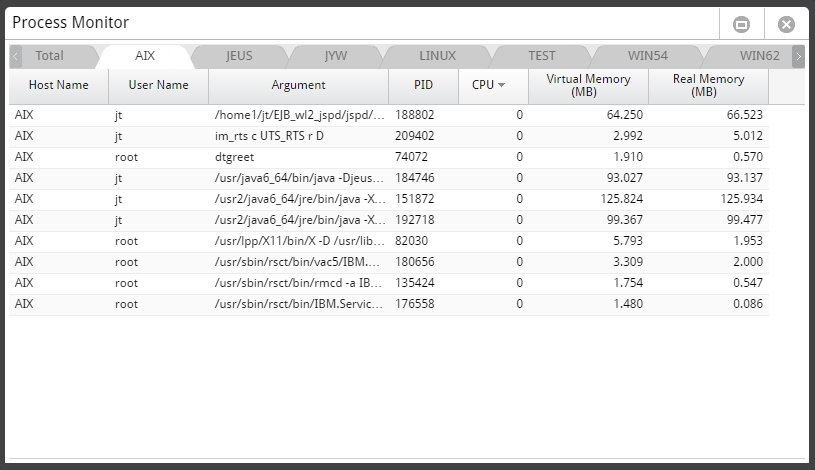
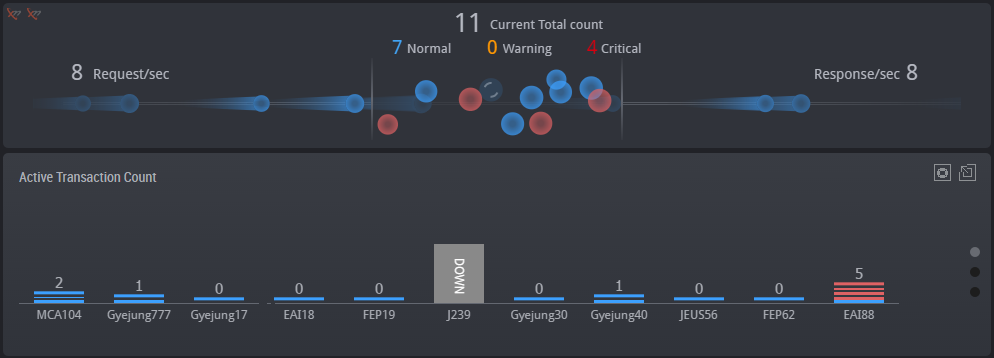
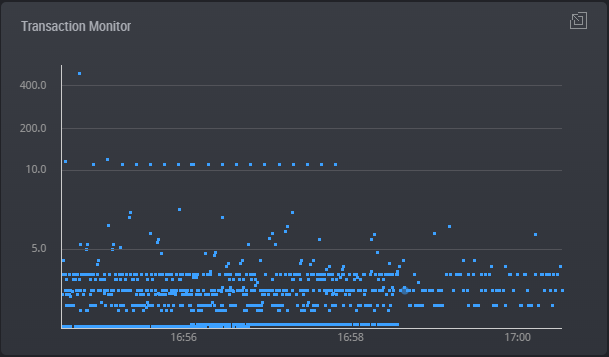
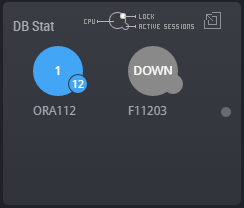
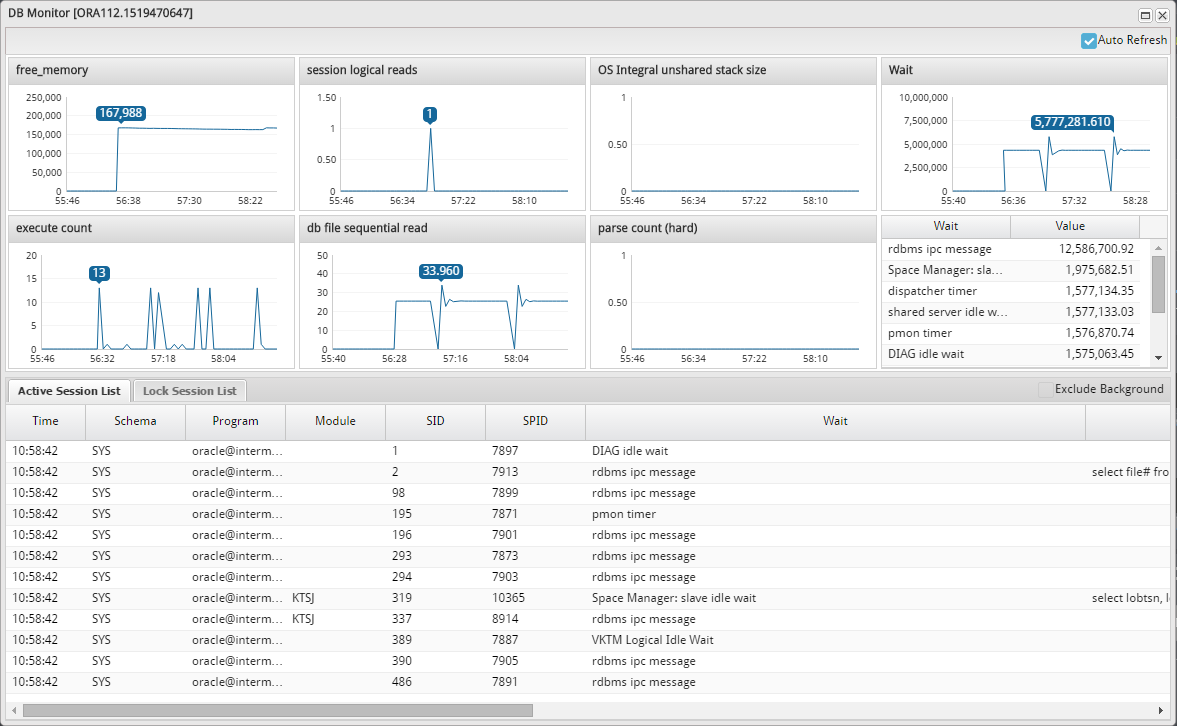
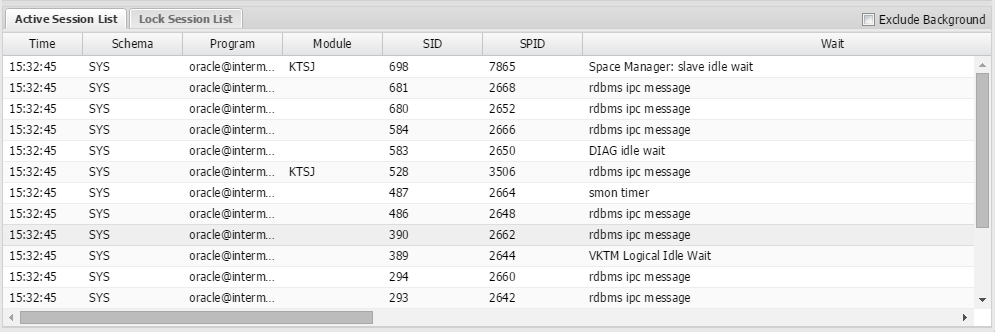
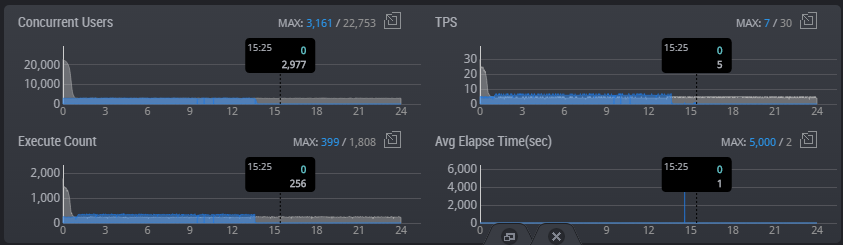
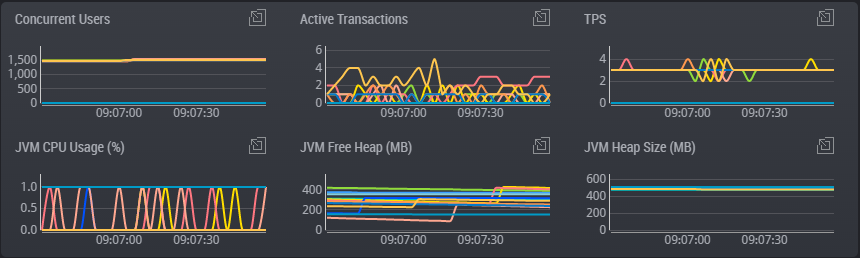
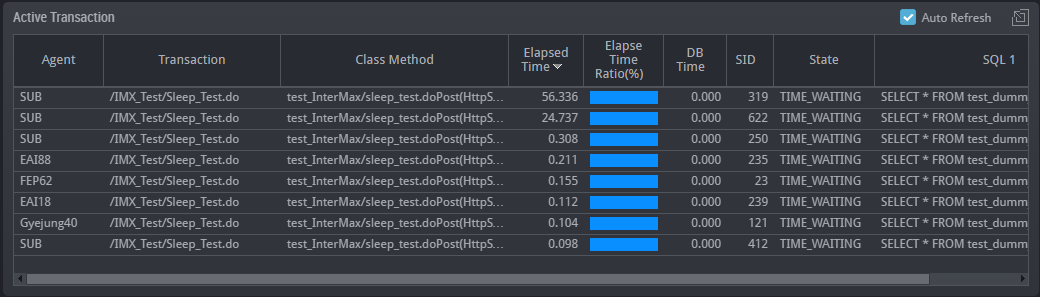
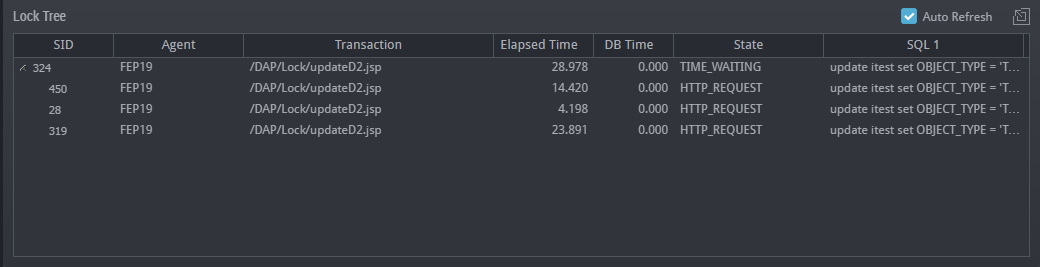
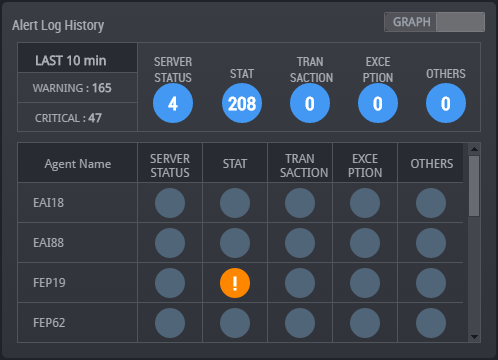
The real-time monitoring function enables you to easily and quickly identify in which WAS or DB the system error occurred or the performance degradation occurred, among the many servers which make up the web service.